TraceTheMap - 8kSec
Description:
TraceTheMap is an iOS location-based challenge where you must collect 5 hidden map markers scattered within a 1 km radius. Each collectible is worth 100 points—and you need all 500 to win. Get within 50 meters of each collectible to score. Sounds simple? Not so fast. While spoofing your GPS might seem like the obvious path, this app comes with a few built-in countermeasures to detect foul play. From unexpected location sanity checks to behavioral traps, it won’t be a walk in the park—even if you fake it.
Objective:
Score 500 points by collecting all 5 hidden markers using clever spoofing, patching, or dynamic instrumentation—without triggering the anti-cheat logic.
Restrictions:
- The win page is only after scoring 500 points.
- The app performs runtime checks to detect spoofing and other manipulations.
Explore the application
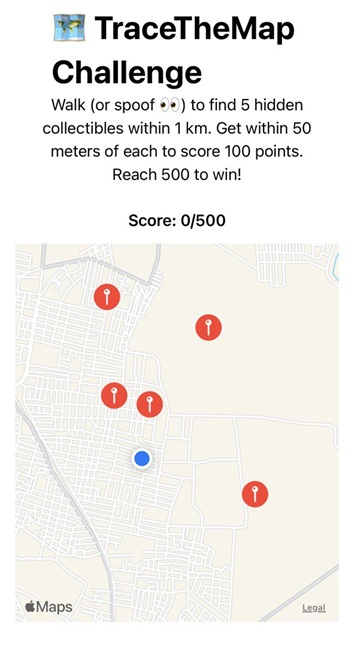
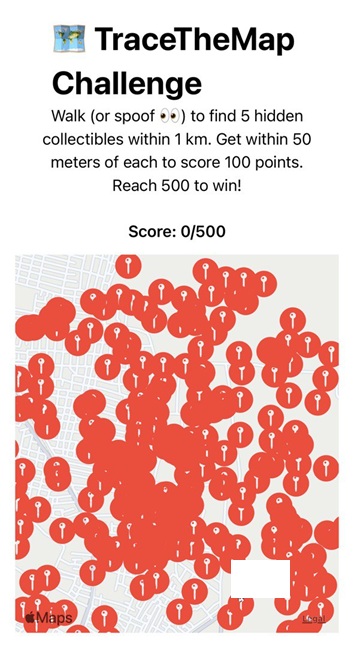
When the app launches, it shows your current location on the map, marked along with five Map markers placed within a 1-kilometer radius.
-[CLLocation coordinate] is an instance method provided by Core Location’s CLLocation class that returns the point coordinate of a CLLocation object. The return type is a C struct.
When an app has a CLLocation instance (for example, received from CLLocationManager), calling location.coordinate yields a CLLocationCoordinate2D struct containing the latitude and longitude values.
How apps typically obtain location
There are two common patterns:
Delegate-based updates The app registers a delegate with
CLLocationManagerand receives updates via:1
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray<CLLocation *> *)locations;
In this pattern the app reads
locations.lastObject.coordinateor similar.Polling / getter calls The app may synchronously call
-[CLLocationManager location]or call-[CLLocation coordinate]onCLLocationobjects obtained from other APIs (for exampleMKUserLocation), effectively polling the current coordinate.
The idea behind location spoofing
Location spoofing means causing an application to receive fabricated location data instead of the device’s true GPS coordinates. The objective can be testing, QA, or development scenarios where simulating movement or different geographies is required without physically moving the device.
Approaches fall into two categories:
- Injection of fake delegate updates Intercept or emulate
CLLocationManagerbehavior and call the delegate methodlocationManager:didUpdateLocations:with fabricatedCLLocationobjects. This causes the app to behave as if it received genuine location updates. - Hooking getters / return values Intercept methods that return location data, such as
-[CLLocation coordinate],-[CLLocationManager location], or-[MKUserLocation location], and modify their return values so callers receive spoofed coordinates.
The script attempts to spoof location coordinates by intercepting -[CLLocation coordinate] with Frida and replacing the method’s return value with a new coordinate (the supplied spoof_latitude / spoof_longitude). After loading the script and calling spoof_location(lat, lon), any code that calls location.coordinate should receive the spoofed values.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
function spoof_location(spoof_latitude, spoof_longitude)
{
var hook_cllocation = ObjC.classes["CLLocation"]["- coordinate"]
Interceptor.attach(hook_cllocation.implementation, {
onLeave: function(return_value) {
//console.log(new ObjC.Object(return_value))
var spoofed_return_value = (new ObjC.Object(return_value)).initWithLatitude_longitude_(spoof_latitude, spoof_longitude)
return_value.replace(spoofed_return_value)
}
});
}
//Mention latitude and longitude in below function call
spoof_location(46.211275,2.368013)
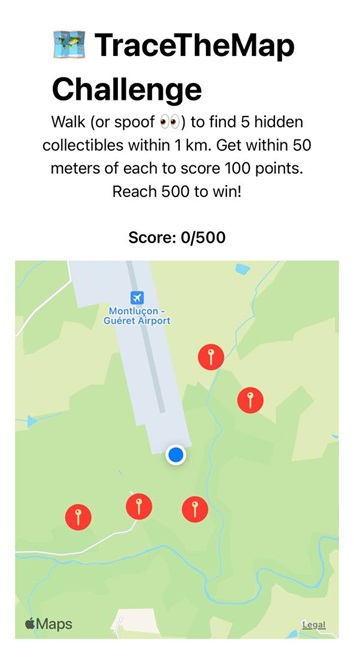
After spawning the app with the Frida script, the device location was spoofed to a point in Paris. I should spoof my location to simulate moving toward the map markers on the map to collect them.
This script allows dynamic GPS location spoofing on iOS by overriding the system’s CLLocation coordinates through Frida. It enables you to simulate movement in any direction by specifying a distance in meters.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// Base coordinates
var spoof_latitude = 46.211275;
var spoof_longitude = 2.368013;
function spoof_location(lat, lon) {
var hook_cllocation = ObjC.classes["CLLocation"]["- coordinate"];
Interceptor.attach(hook_cllocation.implementation, {
onLeave: function (ret) {
var spoofed = (new ObjC.Object(ret)).initWithLatitude_longitude_(lat, lon);
ret.replace(spoofed);
}
});
}
// Convert meters to degrees (approx)
function metersToDegrees(m) {
return m / 111111; // ~111.111 km per degree latitude
}
function right(m = 50) {
spoof_longitude += metersToDegrees(m);
spoof_location(spoof_latitude, spoof_longitude);
}
function left(m = 50) {
spoof_longitude -= metersToDegrees(m);
spoof_location(spoof_latitude, spoof_longitude);
}
function up(m = 50) {
spoof_latitude += metersToDegrees(m);
spoof_location(spoof_latitude, spoof_longitude);
}
function down(m = 50) {
spoof_latitude -= metersToDegrees(m);
spoof_location(spoof_latitude, spoof_longitude);
}
// Initial spoof
spoof_location(spoof_latitude, spoof_longitude);
How It Works
The script hooks into the
CLLocation -coordinatemethod and replaces its return value with custom latitude and longitude values.The starting location is defined by two global variables:
1 2
spoof_latitude = 27.1782936; spoof_longitude = 78.0474205;
The
spoof_location(lat, lon)function applies the spoofed coordinates to the device.A helper function
metersToDegrees(m)converts meters to geographic degrees (approximation: 1° ≈ 111,111 meters).Directional functions allow simulated movement:
right(m)→ Move east by m metersleft(m)→ Move west by m metersup(m)→ Move north by m metersdown(m)→ Move south by m meters
Each function defaults to 50 meters if no value is provided.
Example Usage
1
2
3
4
right(40); // Move 40 meters east
left(10); // Move 10 meters west
up(); // Move 50 meters north (default)
down(100); // Move 100 meters south
Spawn the application with the Frida script, then use the directional functions to navigate to the map markers on the map.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
└─# frida -U -f com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z -l 8ksec.js
____
/ _ | Frida 16.1.4 - A world-class dynamic instrumentation toolkit
| (_| |
> _ | Commands:
/_/ |_| help -> Displays the help system
. . . . object? -> Display information about 'object'
. . . . exit/quit -> Exit
. . . .
. . . . More info at https://frida.re/docs/home/
. . . .
. . . . Connected to iOS Device (id=4a6e3de083155aae4c1a3473ff2d8c76b254887b)
Spawned `com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z`. Resuming main thread!
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> down(100)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> down(100)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> down(100)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> down(50)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> right(50)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> right(50)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> down()
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> down(20)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> right(20)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> right(20)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> right(20)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> right(20)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> left(20)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> left(20)
[iOS Device::com.8ksec.TraceTheMap.W46SY5ZJ6Z ]-> down(20)
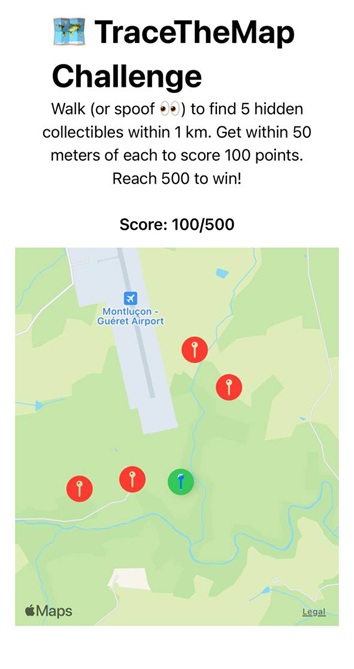
Once you reach a map marker, it will turn green and your score will increase by 100.
Keep using the directional controls to visit each of the five map markers and achieve a score of 500 to win.
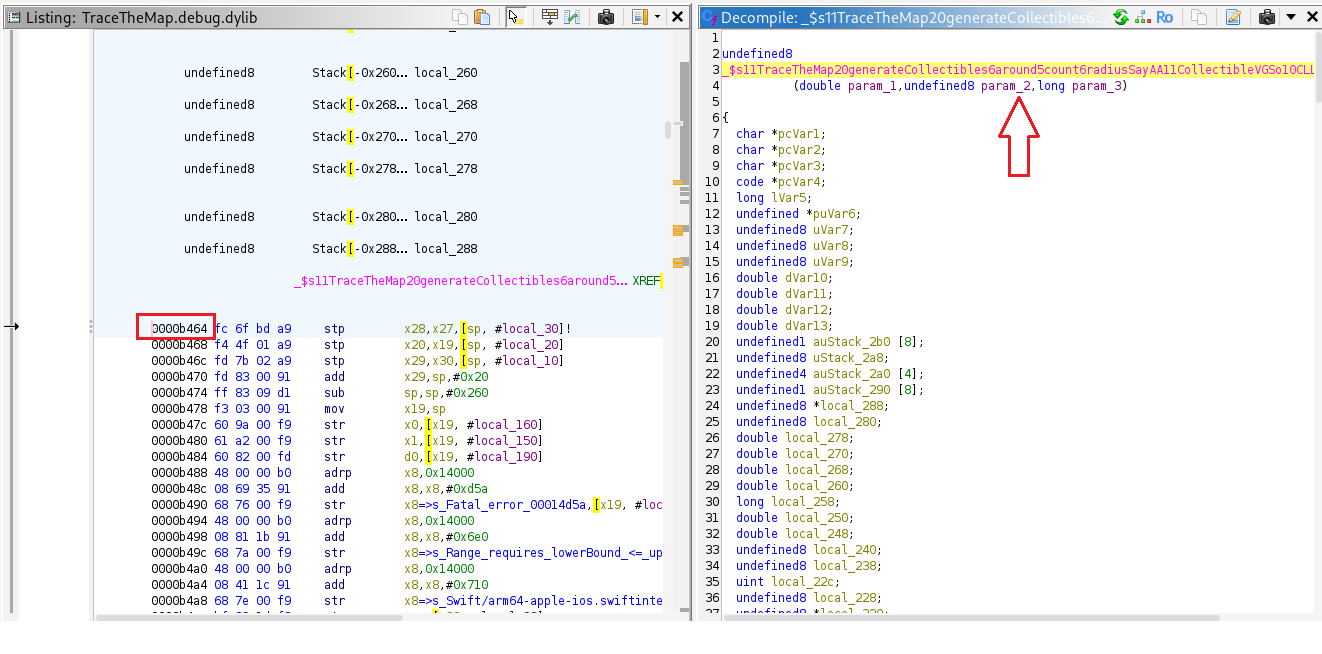
To simplify collection, hook parameter 2 and overwrite its value from 5 map markers to a larger number so we can collect more markers easily.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
var offset = ptr('0xb464');
var t_module = 'TraceTheMap.debug.dylib';
var base = Module.getBaseAddress(t_module);
if (base === null) {
throw new Error('Module not found: ' + t_module);
}
var target = base.add(offset);
Interceptor.attach(target, {
onEnter: function (args) {
args[1] = ptr(0x100); // 256 in decimal
}
});
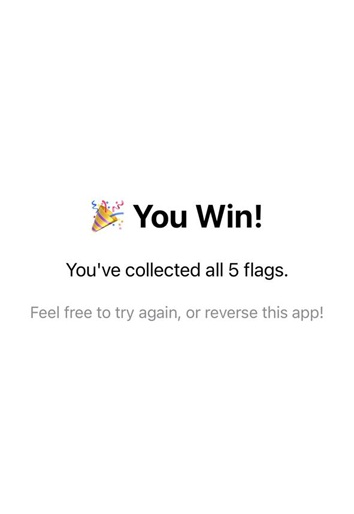
You can now collect all five map markers with a single move and win
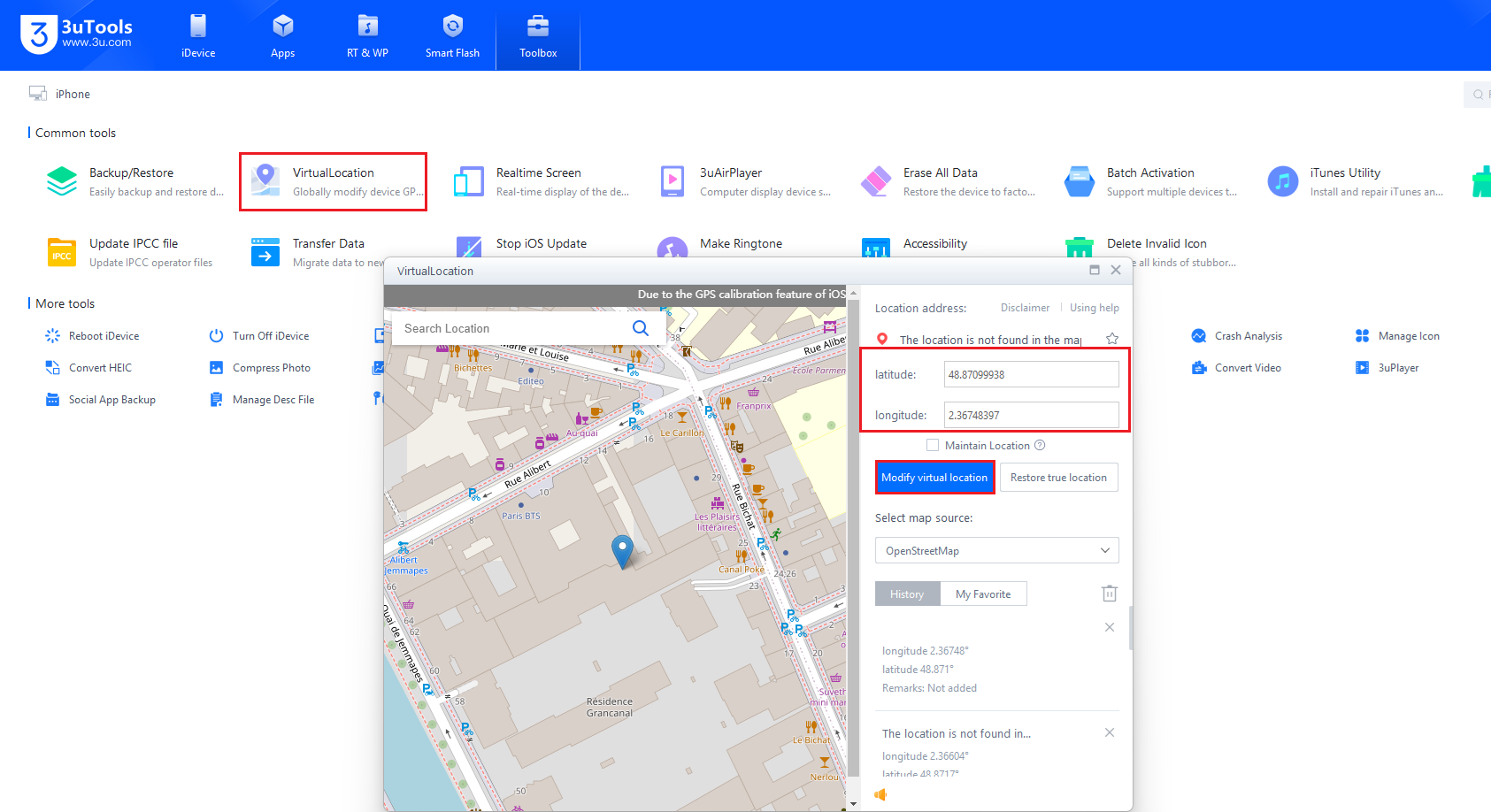
Bonus: Location Spoofing With 3uTools
3uTools provides a “Virtual Location” feature that can set an iOS device’s reported GPS coordinates from a connected Windows PC. When activated, apps on the device that request location data will see the spoofed latitude/longitude instead of the device’s actual GPS coordinates.
Install 3uTools on a Windows PC and connect the iPhone to the PC via USB.
Open 3uTools, go to Toolbox → Virtual Location (or similar menu), select a point on the map or enter latitude/longitude, and apply the change.
Once applied, the device reports the selected coordinates to location-aware apps until the spoof is disabled or the device/app updates its state.
When you select new latitude and longitude values in 3uTools, the app updates its location accordingly. Continue updating the coordinates to reach all the map markers.