FactsDroid - 8kSec
Description
Craving a smarter way to soak up bite-sized knowledge? Say hello to FactsDroid, your sleek and modern companion for discovering mind-blowing facts anytime, anywhere. Built with a stunning Material 3 design and fluid animations, FactsDroid curates random facts from reliable sources and presents them in an engaging, informative format.
Love what you learn? Rate each fact using a 5-star system and save your favorites to a private vault. Thanks to its encrypted local database, your fact collection stays secure and just for you.
Wrapped in vibrant gradients and an intuitive layout, FactsDroid turns everyday curiosity into a fun, stylish experience.
Objective
Learn the art of network interception. Your goal is to intercept the network traffic generated by FactsDroid in a tool that supports dynamic tampering with network traffic such as Burp Suite or Charles Proxy. You should be able to view and modify the API requests and responses between FactsDroid and the backend server without statically patching the provided APK.
Successfully implement a Machine-in-The-Middle (MITM) attack that allows you to manipulate the facts being displayed to the user, potentially inserting custom content or modifying the retrieved facts before they reach the application.
Successfully completing this challenge demonstrates important skills in network security analysis, understanding of mobile app API interactions, and highlights the importance of proper certificate validation and network traffic encryption in mobile applications.
Explore the application
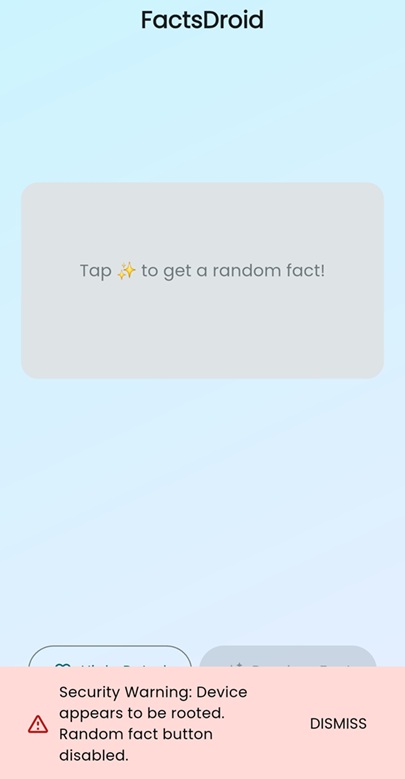
FactsDroid is a Flutter Android application that fetches facts from a remote API. It implements root detection and disables the fact-loading functionality when running on a rooted device
Analyzing the application using JADX
From: B.a.g
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
public void mo1g(C0001a c0001a, C0114j c0114j) {
boolean z2;
boolean z3;
boolean z4 = true;
int i2 = MainActivity.f508g;
AbstractC0258h.m429e((MainActivity) this.f0b, "this$0");
AbstractC0258h.m429e(c0001a, "call");
if (!AbstractC0258h.m425a((String) c0001a.f4c, "isDeviceRooted")) {
c0114j.m306b();
return;
}
String str = Build.TAGS;
if (str == null || !AbstractC0373g.m565M(str, "test-keys")) {
String[] strArr = {"/system/app/Superuser.apk", "/sbin/su", "/system/bin/su", "/system/xbin/su", "/data/local/xbin/su", "/data/local/bin/su", "/system/sd/xbin/su", "/system/bin/failsafe/su", "/data/local/su", "/su/bin/su"};
int i3 = 0;
while (true) {
if (i3 >= 10) {
Process process = null;
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"/system/bin/getprop", "ro.debuggable"});
String readLine = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream())).readLine();
z2 = readLine != null ? AbstractC0373g.m565M(readLine, "1") : false;
process.destroy();
} catch (Throwable unused) {
if (process != null) {
process.destroy();
}
z2 = false;
}
if (!z2) {
try {
Process exec = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"su"});
if (exec != null) {
exec.destroy();
}
z3 = true;
} catch (Throwable unused2) {
z3 = false;
}
if (!z3) {
z4 = false;
}
}
} else if (new File(strArr[i3]).exists()) {
break;
} else {
i3++;
}
}
}
c0114j.m307c(Boolean.valueOf(z4));
}
This function handles a call named isDeviceRooted. If that call is received, it performs several common root-detection checks on the device and returns true or false back to the Flutter side.
Specifically, it:
- Checks for the presence of known SU/Superuser paths (e.g.,
/system/xbin/su,/system/app/Superuser.apk). - Checks the system
ro.debuggableflag to see if the device is in a debuggable/development mode. - Attempts to execute the
subinary, which indicates root if execution succeeds.
If any of these checks succeed, it concludes the device is likely rooted and returns true. Otherwise, it returns false.
Root Detection Bypass 1
By using this Frida script, we can bypass the root check by intercepting the method and invoking g() with no arguments, preventing the original detection logic from executing properly.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Java.perform(function() {
let C0000a = Java.use("B.a");
C0000a["g"].implementation = function (c0001a, c0114j) {
console.log(`C0000a.mo1g is called: c0001a=${c0001a}, c0114j=${c0114j}`);
this["g"]();
};
});
Root Detection Bypass 2
From: O.j.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/* renamed from: c */
public final void m307c(Object obj) {
switch (this.f345a) {
case 0:
((C0115k) this.f347c).f349b = (byte[]) this.f346b;
break;
default:
((C0093g) this.f346b).mo111a(((InterfaceC0131k) ((C0027a) ((C0001a) this.f347c).f5d).f93c).mo316f(obj));
break;
}
}
When the device is detected as rooted, the O.j.c method gets invoked with a true value as its parameter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Java.perform(function() {
let C0114j = Java.use("O.j");
C0114j["c"].implementation = function (obj) {
console.log(`C0114j.m307c is called: obj=${obj}`);
this["c"](obj);
};
});
output
1
C0114j.m307c is called: obj=true
We can bypass root detection by hooking this method and forcing the argument to false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Java.perform(function() {
let C0114j = Java.use("O.j");
var booleanClass = Java.use("java.lang.Boolean");
var falseValue = booleanClass.$new(false);
C0114j["c"].implementation = function (obj) {
console.log(`C0114j.m307c is called: obj=${obj}`);
this["c"](falseValue);
};
});
Once the root check is bypassed, the button that loads the facts becomes enabled
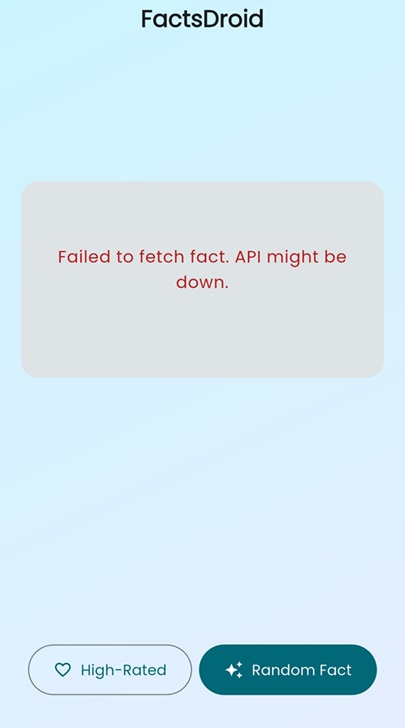
I received this error when I clicked the ‘Random Fact’ button
I used the disable-flutter-tls.js Frida script to turn off Flutter’s TLS verification. After that, I configured Burp Suite by setting the proxy listener to bind on all interfaces and enabling invisible proxying.
Burp configuration step:
- Open Burp Suite → Proxy → Proxy Settings
- Edit the listener on port 8080 (or create a new one)
- Change Bind to address →
All interfaces - Check Enable invisible proxying from the Request Handling tab
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
frida -U -f com.eightksec.factsdroid -l hookFactsDroid.js -l disable-flutter-tls.js
____
/ _ | Frida 17.3.0 - A world-class dynamic instrumentation toolkit
| (_| |
> _ | Commands:
/_/ |_| help -> Displays the help system
. . . . object? -> Display information about 'object'
. . . . exit/quit -> Exit
. . . .
. . . . More info at https://frida.re/docs/home/
. . . .
. . . . Connected to SM A175F (id=RKGYC01YX4H)
Spawning `com.eightksec.factsdroid`...
[+] Pattern version: May 19 2025
[+] Arch: arm64
[+] Platform: linux
[ ] Locating Flutter library 1/5
Spawned `com.eightksec.factsdroid`. Resuming main thread!
[SM A175F::com.eightksec.factsdroid ]-> [ ] Locating Flutter library 2/5
[+] Flutter library located
[+] ssl_verify_peer_cert found at offset: 0x70af3c
[+] ssl_verify_peer_cert has been patched
[SM A175F::com.eightksec.factsdroid ]->
route all device traffic through Burp, run the following iptables commands from an adb shell.
1
2
3
adb shell
# iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j DNAT --to IP:8080
# iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to IP:8080
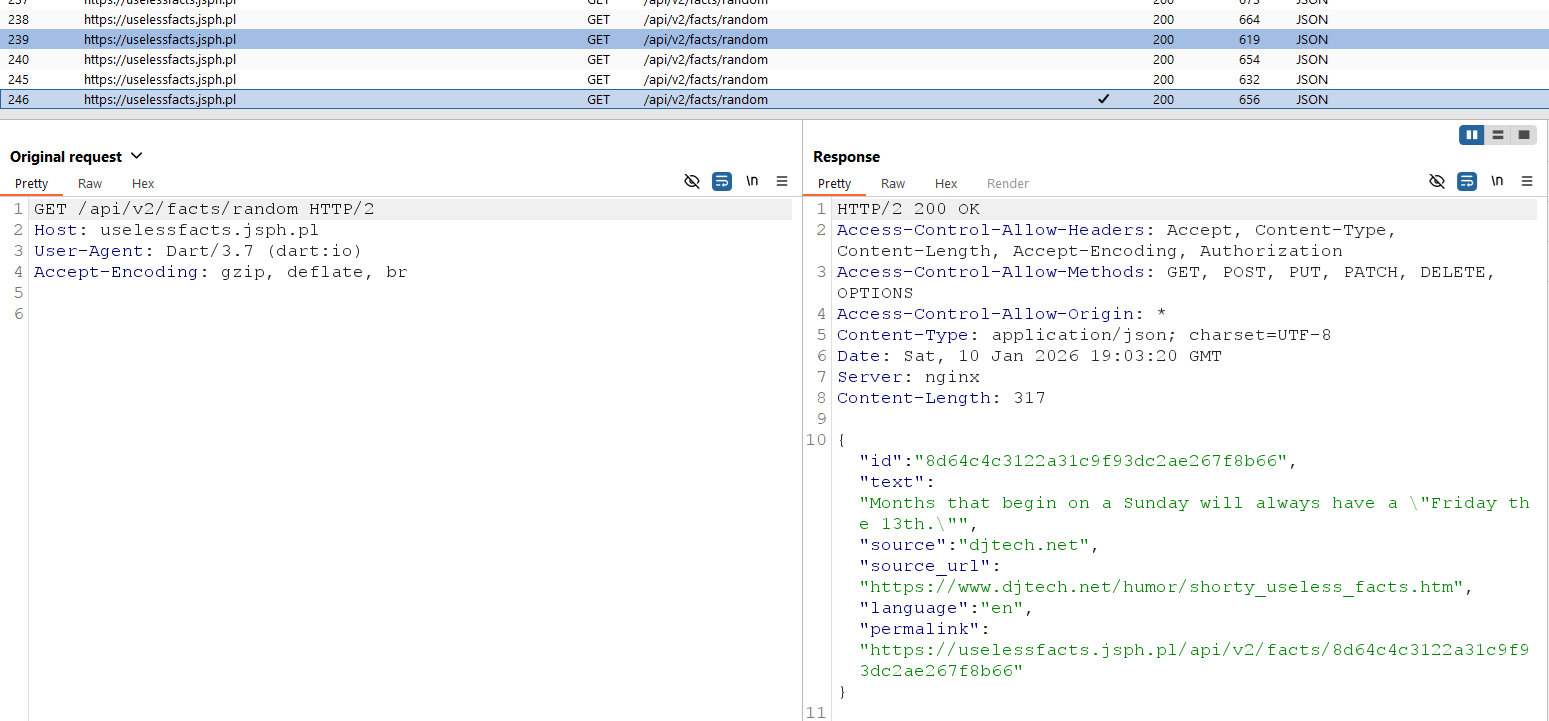
You can now view the app’s traffic in Burp and intercept or modify its requests.
Flush the NAT table to remove the redirection rules.
1
# iptables -t nat -F